Bacterial Conjunctivitis
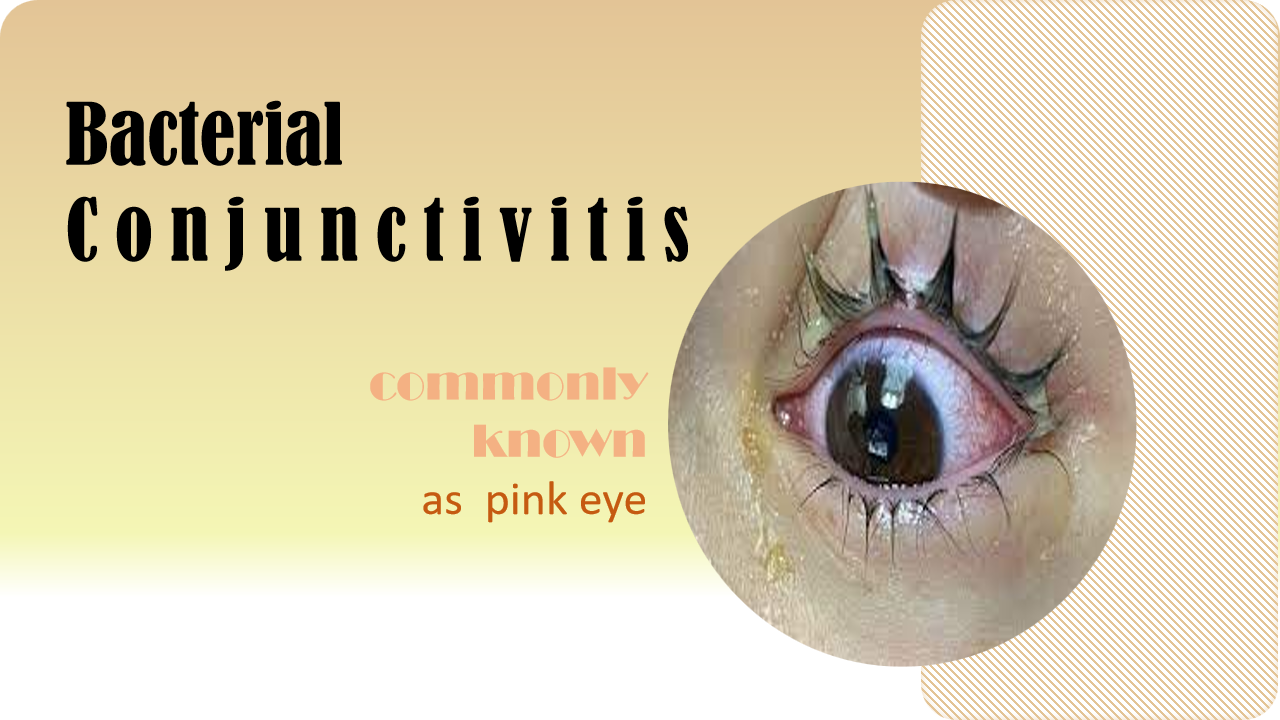
Conjunctivitis is an eye infection. Conjucntivitis is caused by bacteria and virus. Allergens such as pollen or animal hair (infected cat, dog) also cause conjunctivitis. In conjunctivitis, the eye becomes pinkish or reddish. The bacteria that causes the conjunctivitis is called bacterial conjunctivitis. Bacteria infect the conjunctiva. Conjunctiva is the thin layer that covers inside of eyelid and white ball of eye(sclera). Conjunctiva is a protective layer of the eye, that produces mucus and tears. If the infection of conjunctiva spread, its cause perforation(gonococal infection)
Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Group A streptococcus, streptococcus Pseudomonas, E.coil, these are the causative organisms to cause conjunctivitis. People who have suffered from the bacterial conjunctivitis feel redness, pain, little blur to vision. Viral conjunctivitis mostly affects adults, while most children are affected by bacterial conjunctivitis. Both viral and bacterial infections spread among between people. If a new born baby suffers from conjunctivitis, is called neonatal conjunctivitis. Typically, conjunctivitis is cured in one or two weeks, but a long time infection may lead to serious problems in the eye.
Symptoms
- Redness in one or both eyes
- Itchiness in one or both eyes
- A gritty feeling in one or both eyes
- A discharge in one or both eyes that forms a crust during the night that may prevent your eye or eyes from opening in the morning
- Tearing
- Sensitivity to light
- swelling of the conjunctiva
- Watering of the eyes
- Irritation
- pain
Cause/Risk factor
- Viruses
- Bacteria
- Allergies(pollen, perfume, cosmetics, smoke, dust mites)
- A chemical splash in the eye
- A foreign object in the eye
- Exposure to someone infected with the viral or bacterial form of conjunctivitis
- Exposure to something you're allergic to, for allergic conjunctivitis
- Using contact lenses, especially extended-wear lenses
- Infected eye drops
- Contaminated contact lenses
Diagnosis
Cytology examination:
A cytology test is performed to diagnose the bacterial conjunctivitis. Which microorganisms are responsible for the bacterial conjunctivitis that are diagnosed by the cytology test. The specimen is obtained from an eye swab. Swab is a technique, in which fluid or push samples are collected from the eye by the cotton bud. The cytology test is coupled with microscopy examination along with staining technique. Gram stain and Geimsa stain are used in the laboratory. Grain stain and Giema stain are used to examine to detect the bacteria and cytology test respectively. Giemsa stain is also used to detect bacteria, fungus, Chlamydia.
Gram negative rods (Pseudomonas) and white cells
Reference:
- https://eyemicrobiology.upmc.com/Cytology.htm
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pink-eye/symptoms-causes/syc-20376355
0 comments