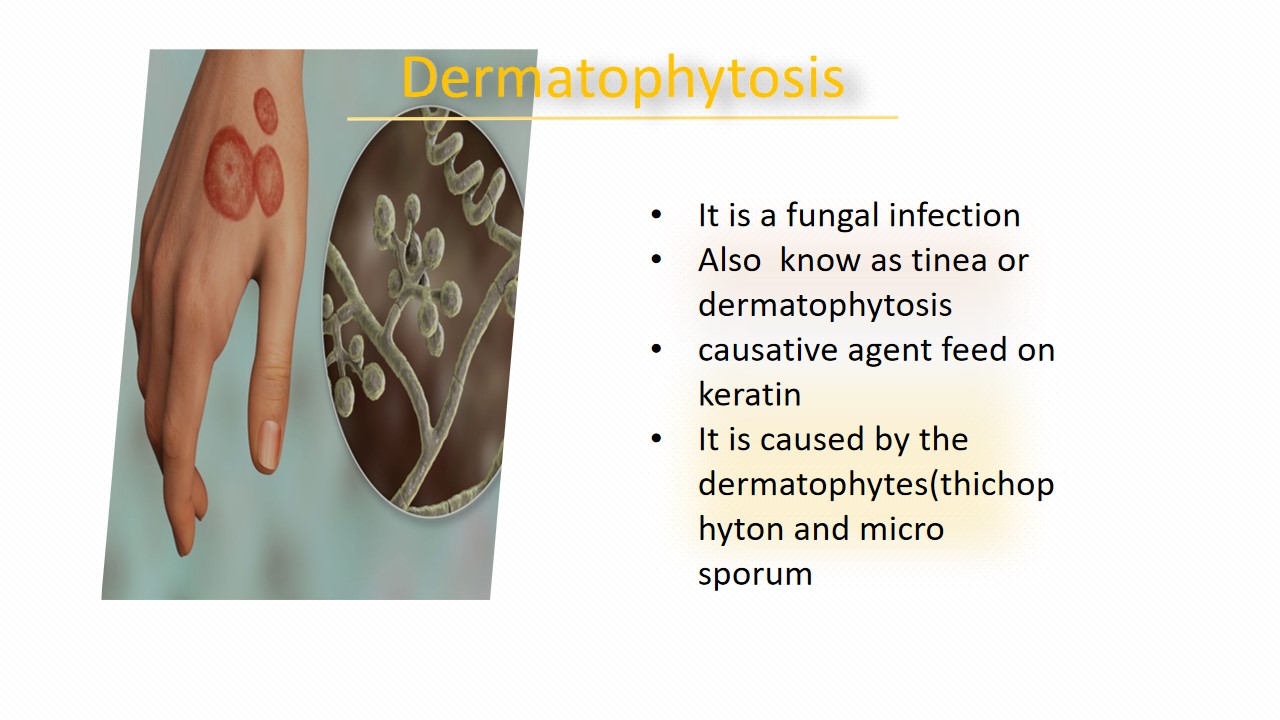
Dermatophytosis
A dermatophyte infection is fungal disease that can affect the skin, hair, and nails. It is also called dermatophytosis or tinea. One of the most frequent causes of superficial fungal infections is tinea infections that most of the people is suffered by it, which are identified by which part of the body affected.
For instant, Ringworm or tinea corporis, affects the arms, trunk, and legs. tinea capitis or scalp ringworm, affects the scalp and hair shafts. tinea faciei affect the facial skin. Jock itch ortinea cruris, affects the groin and inner thighs. Athlete's foot or tinea pedis andtinea unguium affects the hands and feet respectively. And tinea barbae affect tofacial hair follicles, affects people who have facial hair. Common names for dermatophyte nail infections include and dermatophyte onychomycosis or tinea unguium. Children, elderly people, and those with weakened immune systems are more vulnerable to contracting dermatophyte infections. The fungi that cause dermatophytosis are several in number. The most frequent cause is dermatophytes, specifically those belonging to the genera Trichophyton and Microsporum. These fungi target different parts of the body.
Symptoms
- red, scaly, itchy or raised patches
- patches may be redder on outside edges or resemble a ring
- patches that begin or develop a blister
- Bald patches may develop when the scalp is affected
Cause/Risk factors
- Dermatophyte Fungi(Trichophyton and Microsporum)
- Direct Contact to infected people
- Fomite Transmission
- Personal Hygiene
- Occupational Exposure
Diagnosis
Microbiology Department: Skin scraping, nails, and hair used as a specimen, keep the specimen on the glass slide and apply potassium hydroxide(KOH) on it, and observe under the microscope.
Skin scrapes observed under a microscope
Diagnosis:
Cytology Department: The specimen was obtained from the lesion(the moist cotton swab rubbed over the active lesion, called scale) from the infected area. Keep this specimen on the glass slide and add a few drops of 10% to 20% KOH(potassium hydroxide). After the wet-mount preparation is completed, then examine it under a microscope. This method helps to visualize hyphae, which are uniformly wide, branching rod-shaped filaments with septa (lines of separation). Tiny dermatophyte spores may be evenly coated on the hair shaft in cases of tinea capitis.
Cytology examination
Reference:
1. https://www.osmosis.org/answers/dermatophyte-infection
2. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dermatophytosis
0 comments