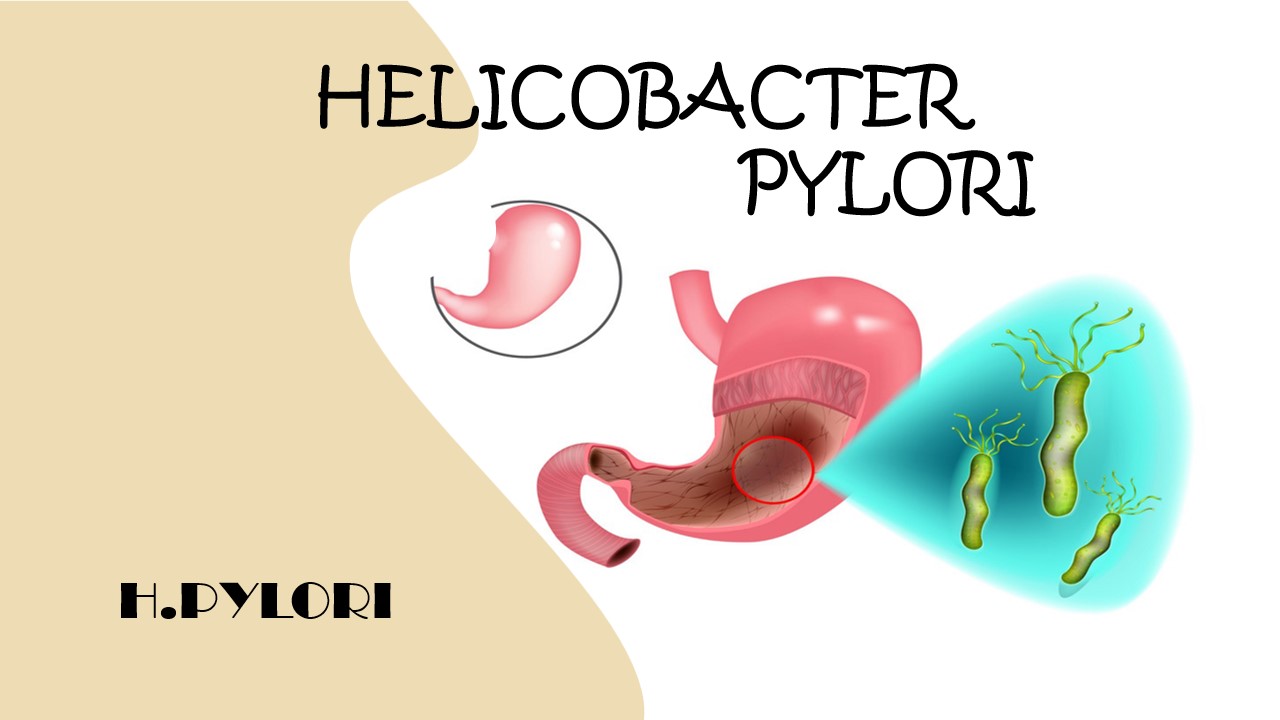
Helicobacter Pylori disease
Helicobacter Pylori is a type of bacteria. Helicobacter pylori is commonly associated with stomach inflammation. Helicobecter pylori is caused a stomach disease. This pathogen caused gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, gastric adenocarcinoma and, duodenum gastric lymphoma. Helicobacter Pylori burrows the stomach cell lining and it turns into gastritis , also infects the upper part of the intestine (duodenum). Helicobacter pylori bacteria is mainly the cause of gastritis and peptic ulcers.The risk of stomach cancer increases when ulcers occur again and again for a long time.
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped, gram-negative organism. The infection acquired during childhood. This is common among children but increased age of 60. Helicobactor pylori produces ammonia. Amonnia is enable the organism to grow in stomach and erode the mucosal barrier. Helicobacter pylori is produce cytotoxin and mucolitic enzyme that are play a vital role in mucosal damage and ulcerogenesis. Sometimes the symptoms of Helicobacter pylori are not identified. People who have the infection of Helicobacter pylori oftencomplainof vomiting with blood,loss of ape tide and diarrhea. This disease is a contagious disease, It is spread by others when contact with an infected person by sharing the same toilet, contact with saliva and other body fluid of an infected person.The diagnosis of H.pylori is carried by gastroscopy and bacteria and organism has been cultured from stool, saliva, dental plaque.
Symptoms
- Bloating
- Burping
- No appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Weight loss for no clear reason
- Black poop
- Loss of appetite
- Feeling full after you eat just a small amount
Cause/Risk factor
- Dirty food, water, or utensils
- Contaminated poop or vomit
- Crowded living conditions
- Lack of clean water and sewer service
- Living in close quarters with someone who is infected
- Living in a developing country
Diagnosis:
Microbiology department: the tissue section of an infected area to take as a specimen. To Swab the infected tissue and make the organism grow on the media plate. Take a small portion of the colony , spread it on the slide and use the stain for microorganism identification observed under the microscope.
Gram staining of H.pylori
Histology department:In pathology lab the pathologist perform rapid urease test (RUT) to detect the helicobacter pylori present or not. But sometimes tests give false positive results. then the pathologist performs histology staining of the biopsy sample.In biopsy, a long, flexible tube with a camera is inserted down through the throat and esophagus into the stomach and duodenum (upper small intestine ) with an endoscope and removes tissue samples from the infected site for biopsy and culture. After that to make a thin slice of infected tissue and stain with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and see under microscope.
Gastric biopsy under microscope to detect Helicobacter pylori disease
References:
- https://consultqd.clevelandclinic.org/assessing-the-diagnostic-value-of-repeat-h-pylori-biopsies
- https://www.mdpi.com/2075-1729/12/11/1789
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007501.htm#:~:text=A%20tissue%20sample%2C%20called%20a,the%20hospital%20or%20outpatient%20center
0 comments