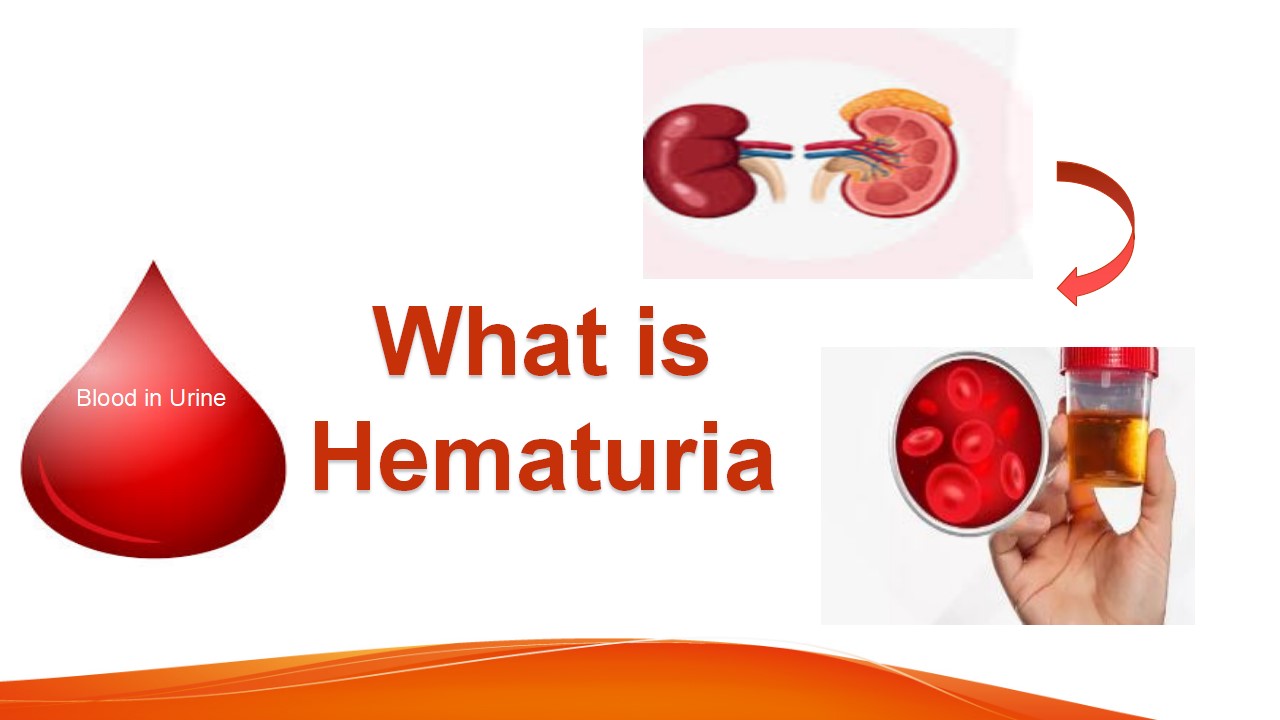
Hematuria
Hematuria is one of the conditions of kidney disease. In hematuria condition, the red blood cells(RBC) are found in the urine. There are a lots of consequences of this, including, infection, kidney disease, vigorous exercise. When the urine looks red or brown while urinating, it means blood is present in the urine is called gross or visible hematuria. Sometimes it is not visible by the nacked eye and it is called microscopic hematouria because it can see by microscopy examination. Blood can be mixed in the urine from any location of the body within the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, prostate(in men). All red urine is not hematuria. The urine shows red because of other factors or substances, such as medication, foods, blackberries, beets, food color or dyes. Mensturation in women is one of the causes of the appearance of red blood cells. The urine dipstick test is the cheapest method to find out the RBC present in the urine, but sometimes it shows false positive results. Urine dipstick test shows the positive hamaturia when couple with microscopy examination.
Microscopic or Macrohematuria, in which 1ml of erythrocyte is found in the 1liter of urine and it is visible during urination. The American Urological Association (AUA) has defined microhematuria as three or more red blood cells per high-power microscopic field in urinary sediment from two of three properly collected urinalysis specific gravity.
Symptoms
- Red, pink or brown colored urine
- Blood clots in urine
- Pain in upper abdomen or pain in back
- Weakness
Causes/Risk factor
- Age
- Kidney infection
- Bladder or kidney stone
- Enlarge prostate
- Cancer
- Kidney injuries
- Urinary tract infection
- Family history
- Certain medicine
- Hard exercise
Diagnosis:
Cytology Depatment
Urine cytology is a test for the detection of hematuria by microscopic examination. This also helps to diagnose other diseases related to kidney or cancer. Urine was collected from the patient. After collection of the specimen then it is sent to the laboratory. The test should start within 2 hours. After the receiving the urine sample the pathologist performed the centrifugation process for urine. After the centrifugation, the sediment and Supernatant are separated out. These sediment are used for microscopy examination and stained with special colored dyes. Staining helps the pathologist to differentiate the cells with the help of a microscope.
Red blood cells, indicating hematuria
Reference:
1.https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/blood-in-urine-causes
2.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hematuria
3.https://www.maxhealthcare.in/our-specialities/urology/conditions-treatments/hematuria-treatment
0 comments