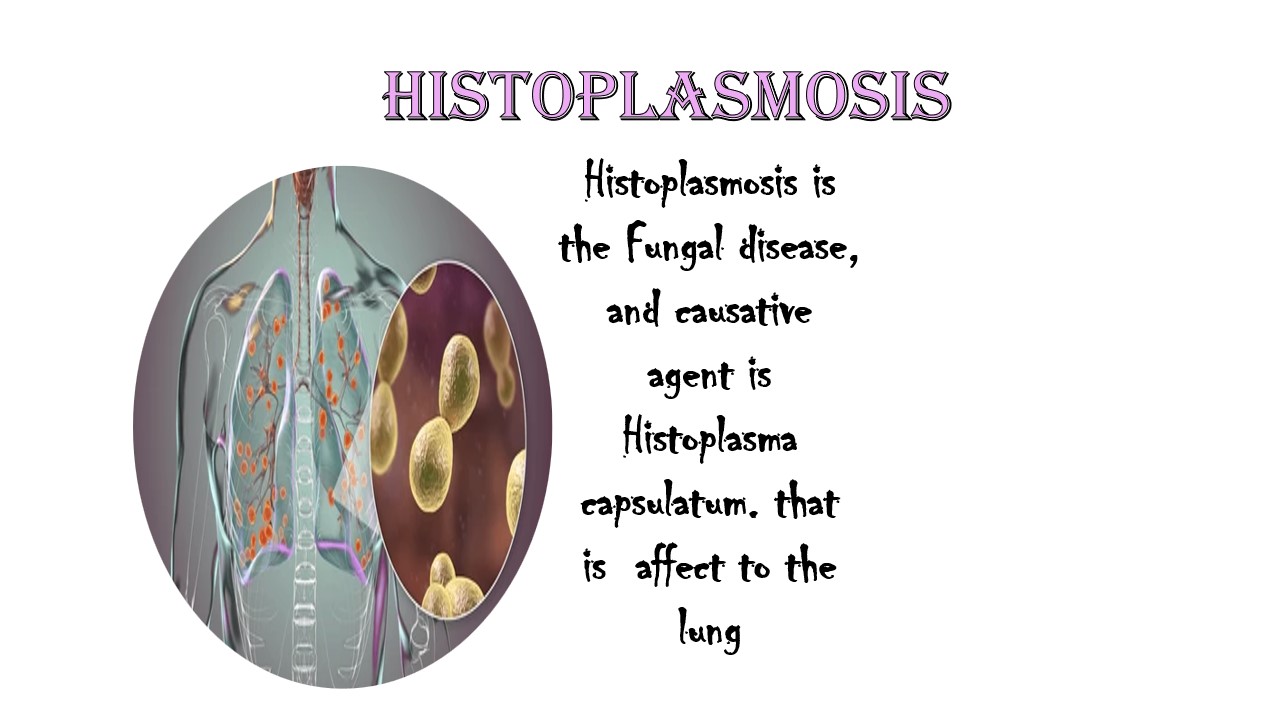
Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis is a fungal disease cause by the histoplasma capsulatum. Which is mainly attaches to the lungs of the body. Histoplasma capsulatum is a fungi, naturally present in the environment, firstly develops as molds then converted into yeast at the room temperature when enter into host cells. Histoplasmosis occure when healthy person inhale tiny airborne spore from the construction site or demolition of building or air contaminated with histoplasma capsulatum or birds and bat dropping.
The three types of histoplasmosis are Acute pulmonary histoplasmosis, chronic cavitary pulmonary histoplasmosis and progressive disseminated histoplasmosis. Acute pulmulary histoplasmosis is a common type of histoplasma capsulatum infection, the symptom like similar to pneumonia, fever cough. Chronic cavitary pulmunaryy histoplasmosis is associated with the patient who have emphysema or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The symptoms include night sweats and weight loss and the symptoms also stay for months or years. Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis is serious form. In which histoplasma capsulatum is spread from the lungs to other parts of the body. This is mainly attack on people who have weakened immune systems or patients have HIV.
Symptoms
- Fever
- Cough
- Sweating
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Chest pain
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Rash or bumps on your lower legs (erythema nodosum)
Cause/Risk factors
- Ohio and Mississippi River valleys
- Exploring caves (spelunking)
- Farming
- Keeping chickens or birds
- Demolition or constructio.
- have a weakened immune system. HIV and immunosuppressive medications are common causes of a weakened immune system
Diagnosis:
Cytology Department: Fine needle aspiration cytology(FNAC), lung aspirate is used in the laboratory to examine abnormalities in the aspirate specimen. Cytology examination along with microscope help to diagnosed the Histoplasmosis
Histoplasma in respiratory fluid sample
Histology Department: For the detection of the histoplasmosis, several methods are available but it take more time . Histopathology examination along with microscope are use to conformation of histoplasmosis. In which the sample is collected from the bone marrow. The collection method is bone marrow aspiration. Then make the smear slide, then apply stain on the slide and observe under a microscope. Under the microscope, yeast showed a round shape and a nucleus in purple colour.
Histopathological examination of Histoplasmosis
References:
1.https://www.msdmanuals.com/en-in/professional/infectious-diseases/fungi/histoplasmosis
2.https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24811-histoplasmosis
0 comments