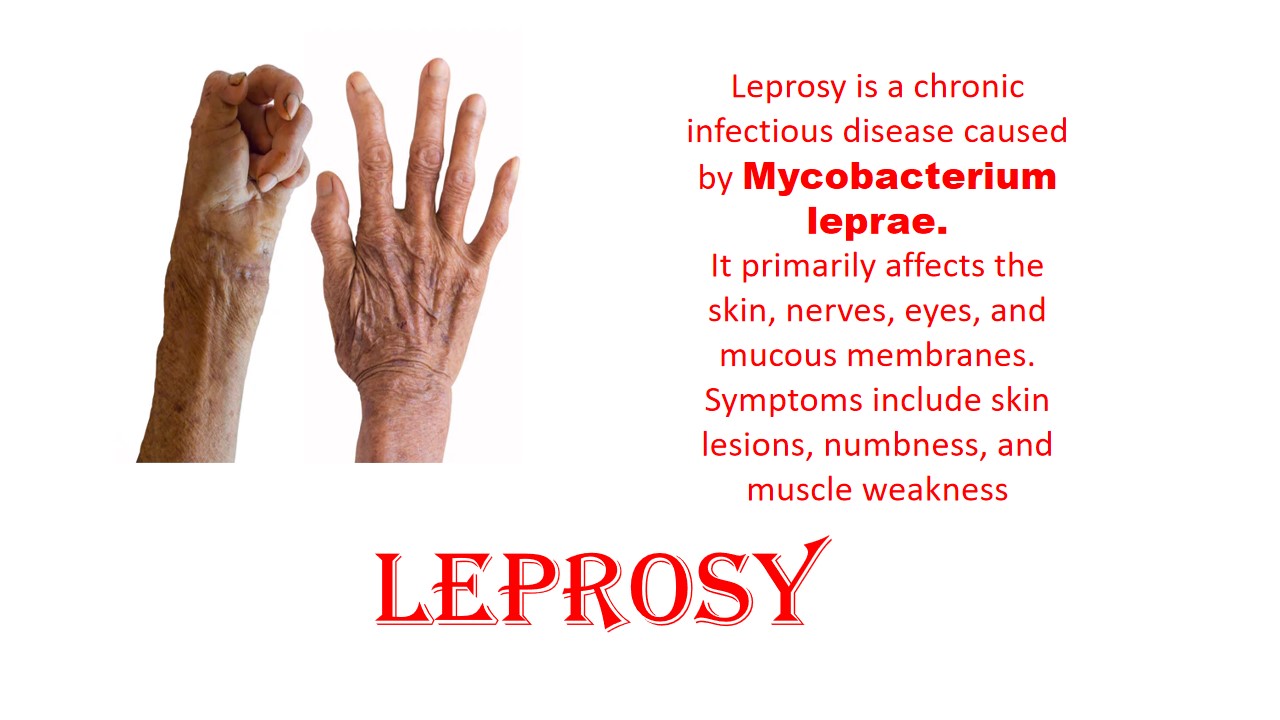
Leprosy
Leprosy is also called Hansen’s disease. Laprasy is chronic infectious disease caused by organism Mycobacterium laprea. Mycobacterium leprea is Gram positive, intracellular, pleumorphic, non-sporing, non-motile, acid fast, pathogenic bacteria.It is primarily affected to the skin, lining of nose, and upper respectory tract. It causes the disfiguring of the skin and nerve damage. In the past, people were worried about leprosy. They thought that it was a contagious, devastating disease, but now people can know that it is hard to spread and easy to treatable.
Leprosy is classified based on the cellular response and clinical finding. Tuberculoid, lepromatous and Borderline these are type of leprosy.Tuberculoid leprosy is not complicated than lepromatous leprosy .Tuberculoid in which skin is consist of few bacteria, centrally hypopigminted macules with sharp raised border. Tuberculoid leprosy is characterized by slight raised skin lesions that are pale or slightly red, the skin has fewer lesions, milder disease, less contagious. Lepromatous and borderline leprosy have poor cell mediated immunity to mycobacterium leprea. Lepromatous leprosy has a systemic infection and may have spread to skin, nerves and other organs, including the nose, testes and kidney. Lepromatous leprosy have more lesion and contagious infection and it also cause peripheral neuropathy, numbness, gynecomastia and also cause lose of eyelashes or eyebrows.Lepromatous leprosy, in which peripheral nerves become thick and more complicated .Borderline leprosy include both tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy, it is less severe , if treatment is left, it will turn to tuberculoid or wil be become as like lepromatous leprosy.
Symptoms
- Dry scalp
- Paralysis or Muscle weakness
- Speech problem
- Nodules on skin
- Painless ulcer on feet
- Light color spots on the skin
- Nerve enlarge
- Growth on skin
- Stiffy, dry and thick skin
- Non-sensitive lesions on body
- Numbness on hands, feet, arms, legs
- Eye problems that might even cause blindness
Cause/ Risk factor
- Close contact with an infected person
- Malnurishment, specific illness , chromosomal mutation also chance to develop leprosy.
- Contact with armadillos (armadillos is a nocturnal insectivorous mammal, it has naturally infected bacteria.)
Diagnosis
Cytology department: FNA specimen used to diagnose leprosy. The samples are spread on the slide and by using the appropriate stain, examined under the microscope.
FNA under the microscope
Microbiology department: The slit skin smear sample is put on the slide and used the specific stain and observed under the microscope to identify the causative microorganism.
Microbiology examination
Histology depaertment
Hensen’s disease is diagnosed by microscopic examination of skin biopsy and or nerve biopsy. To find the bacteria under a microscope. Mycobacterium leprea is not grow on the artificial culture medium. Biopsy specimen taken from the tuberculoid lesion or lepromatous leprosy.
Ziehl-Neelsen Stain(histology)
References:
1.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium_leprae#Pathogenesis
2.https://byjus.com/biology/leprosy/#diagnosis-of-leprosy
0 comments