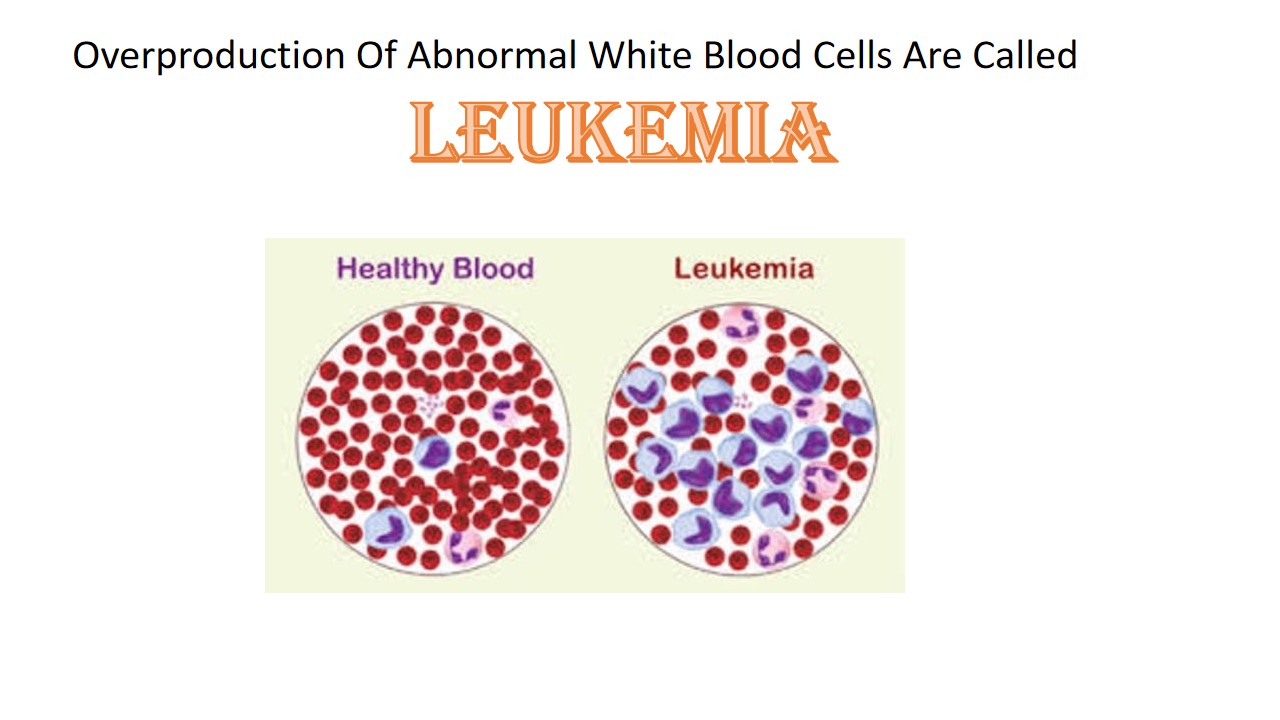
Leukemia
Leukemia is a blood cancer. In the bone marrow, rapid and abnormal growth of cells occurs it leading to the blood cancer called leukemia. Bone marrow is composed of soft and spongy tissue. The luekemia is start in bone marrow. Most of the body blood cells are made in soft spongy tissue of bone marrow. The bone marrow produces mature blood cells that include red blood cells,white blood cells and platelets. Before becoming mature, blood cells go through multiple stages to become fully mature.
In the bone marrow firstly immature stem cell become either lymphoid stem cell or myeloide stem cells. The myeloid stem cell also grow the white blood cells. firstly grow in immature cells, called lymphoblasts then it develop into red blood cell, platelet and certain type of white blood cell such as monocyte and granulocyte (basophils, eosinophils and neutrophile). Lymphoid stem cells are mostly developed white blood cells and natural killer cells, which are also called immune system cells. They firstly become immature white blood cell called lymphoblast then convert into mature white blood cells. The lymphocyte produce B-cells and T-cells. These play an important role in our body. B-cells produce antibodies that act as an army to fight against microorganisms. T -cells, also called helper cells , send signals to immune cells regarding invading of pathogens. The stem cells in the bone marrow could be mutated or changed at any step of development. This type of change may have lead to the leukemia condition. This is caused by DNA mutation .In the leukemia condition, bone marrow produces a lot of white blood cells, the ability of red blood cells and platelets is going to decrease. After leukemia in the body, the immune system becomes weak and the ability of immune cells are affected by unnecessary growth of white blood cells.In this condition, oxygen carried by red blood cells does not reach to the body organ and tissue properly and blood clots do not take place when needed and the body is unable to fight with infectious diseases.
There are four main types and a sub-type of leukemia. The main types are acute lymphocytic leukemia(ALL), acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), chronic lymohocytic leukemia (CLL) and chronic myelogenous leukemia(CML).
Acute lymphocytic leukemia(ALL): ALL is mostly comman in chidren, teen and after the age of 39. Most people are affected by all.
Acute myelogenous leukemia(AML): AML is developing from lymphoide stem cell. It also develops in both children and adults.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia(CLL): CLL, this type of leukemia is develop in slow manner. It is developed from lymphoide stem cells.
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): CML grows from more mature myeloid stem cells. This type of leukemia is slow-growing and rarely found in children and adults.
System
- Feeling fatigued,
- dizzy or cold
- Shortness of breath
- Pale skin
- Headaches
- Recurring infections or difficulty recovering from infections
- Bruises or tiny red or purple spots on the skin
- Bleeding, including frequent or severe nosebleeds, bleeding gums, or heavy menstrual bleeding
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal swelling
- enlarged liver or spleen
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Bone or joint pain
Cause/risk factor
- Smoking
- Previous cancer treatment
- Exposure to industrial chemicals
- Certain genetic disorders
- Mutation in genes
- Family history of leukemia
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of leukemia can be examined in the following ways along with a microscope.
Hematology: The blood smear examined under the microscope.
Normal blood Leukemia under the microscopy
Histology (Bone marrow biopsy): biopsy specimen checked under the microscope to count the cells and look at the shape of the blood cells
Cerebrospinal fluid Blood sample
Cytology (Lumbar puncture): the CSF(cerebrospinal fluid) is the specimen used to diagnose leukemia. The CSF is found in the spinal column. Under a microscope, the CSF sample is examined for indications that leukemia cells have spread to the brain and spinal cord.
Normal marrow aspiration All marrow aspiration
Reference:
1.https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/leptospirosis#how-does-leptospirosis-spread
2.https://www.sprintdiagnostics.in/hyderabad/test/leptospira-detection-by-dark-field-microscopy
0 comments