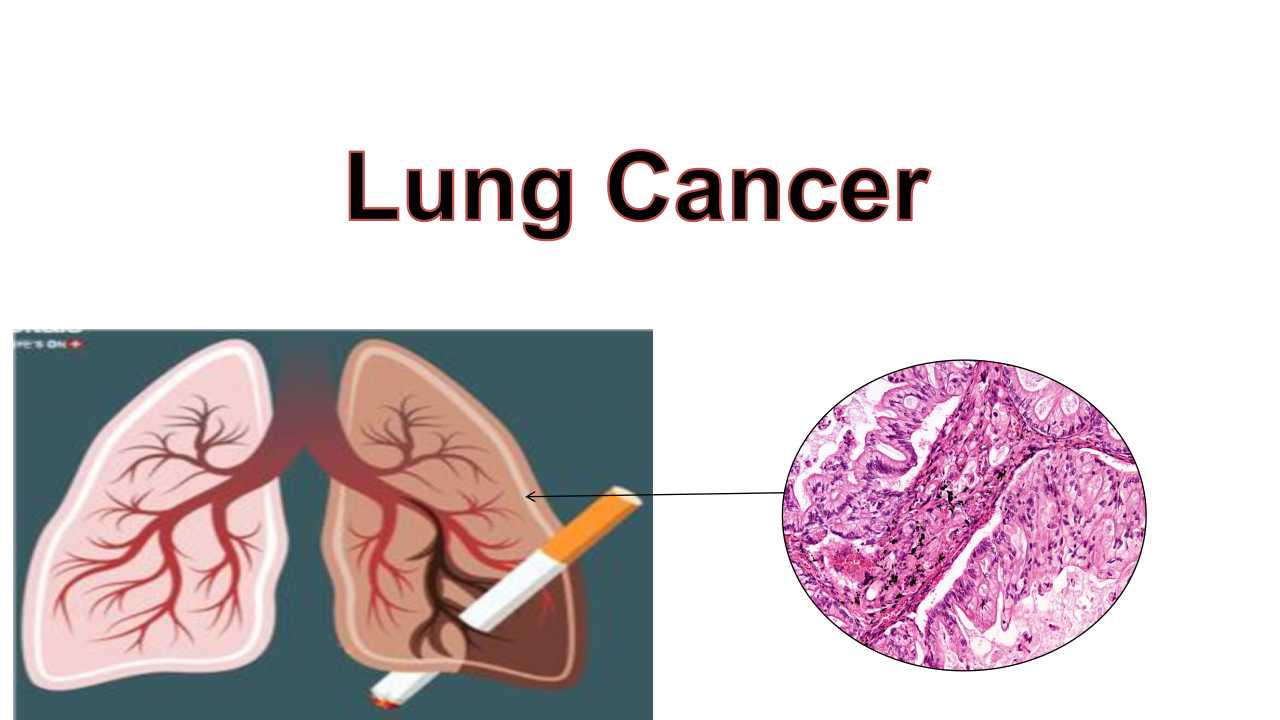
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is a disease caused by the uncontrolled growth or unnecessary cell division in the lung. The person may have a risk of getting lung cancer due to changes in DNA (mutation). Due to mutation, the cells rapidly grow in the lungs as their normal growth. It causes lung cancer. Cancer cells can metastasize from the lung to the other part of the body to affect other organs of the body. lung cancer in which the airway cells are damaged, lungs do not work properly and have problems with breathing and supplying an inadequate amount of oxygen to the body,exchange of oxygen and carbon-dioxide is also disturbing. Lung cancer is widely known as the most dangerous cancer of the lungs.
There are several types of lung cancer, but lung cancer is categorized based on malignant cells seen under the microscope. Such as small cell lung cancer(SCLC) and non -small cells lung cancer(NSCLC). Small cell lung cancer takes place in the center of the lung near to the major airways. This is recognised by the small cell with undefined boundaries, absence of cytoplasm, many mitochondria and have distinctive nuclei with granular looking chromatin and no visible nucleoli.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Non-small cell lung cancer is sub-categorized into three types: adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and large cell carcinoma. Adenocarcinoma: cancer cells produce mucin this is categorized by large shape of clump and resemble of granular in cells. About 40% of lung cancer are adenocarcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma: In which the tumor cells have a layer of keratin and a cavity is shown in the center of the tumor. Large cell carcinoma is a rare carcinoma, According to its name, there is excess cytoplasm, large nuclei. This type of cancer is found in 10% of people. The other type of cancer that start around the lung including lymphomas(cancer in lymph nodes) , sarcomas(cancer in bone and soft tissue), and pleural mesothelioma (cancer in lining of lung).
Symptoms
- Chest pain or discomfort
- A cough that doesn't go away or gets worse over time
- Trouble breathing
- Wheezing
- Blood in sputum (mucus coughed up from the lungs)
- Hoarseness
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss for no known reason
- Fatigue
- Trouble swallowing
- Swelling in the face and/or veins in the neck
Causes/Risk factor
- Smoking
- Air Pollution
- Asbestos fibers
- Radon Gas
- Exposure to carcinogenic chemicals such as chromium
- family history
- Eating unhealthy food
- Lung diseases
Diagnosis
Sputum cytology: Sputum cytology is done to examine the sputum under a microscope to look for cancerous cells. Sputum is different from saliva. Sputum is secreted by the the bronchi and the trachea. Sputum samples is usually used to diagnose the disease along with microscope.
Biopsy(histology): In lung needle biopsy, takes a small amount of tissue of the lung with a special biopsy needle to determine the lung disease or cancer. This sample is stained with special histochemical stains and examine under microscope.
Sputum sample under microscope Lung tissue under microscope
References:-
1.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lung_cancer#Diagnosis
2.https://www.cancer.org/cancer/diagnosis-staging/tests/biopsy-and-cytology-tests/testing-biopsy-and-cytology-samples-for-cancer/special-tests.html
0 comments