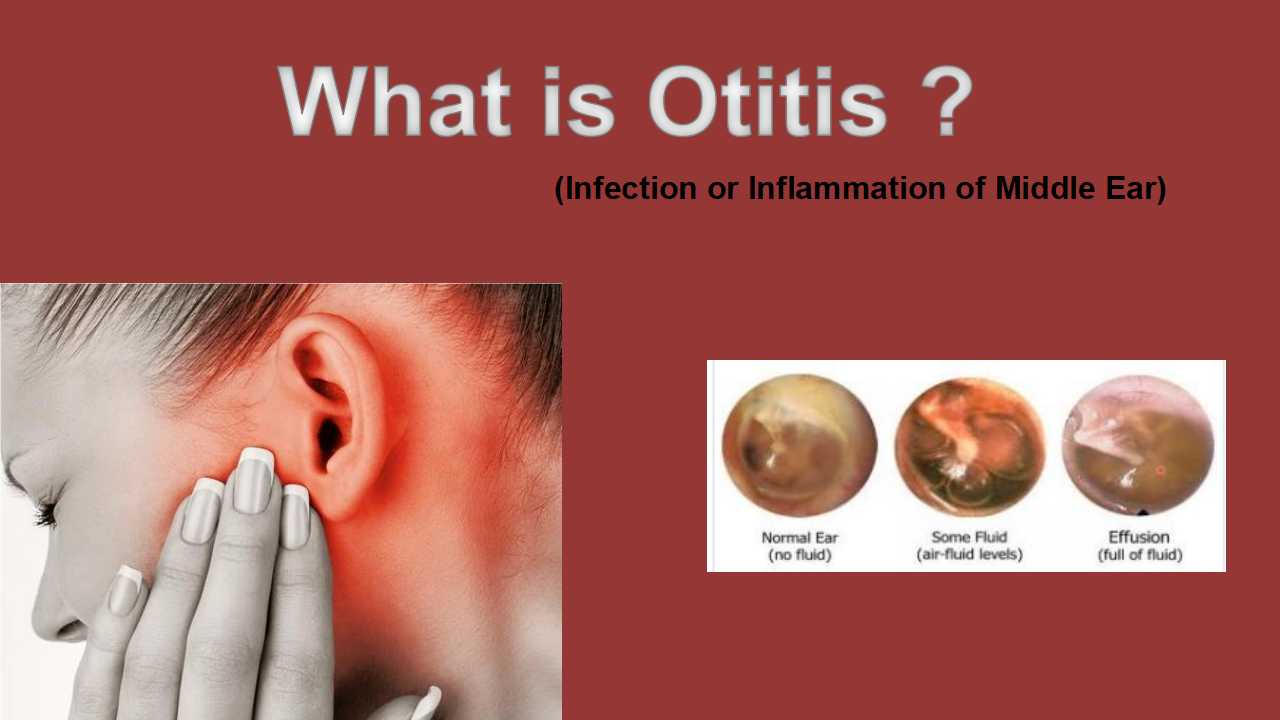
Otitis
Acute otitis media, also knows as ear infection, is an unexpected infection in the middle ear. The air-filled area between the inner ear and eardrum is called the middle ear. It contains the little bones that allow us to hear by sending sound waves from the eardrum to the inner ear. The canals known as eustachian tubes run from the back of the throat to the middle ear. That keeps fluid from building up in the middle ear area and controls the air pressure inside your ear.The viruses and bacteria causes the otitis. Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis, these are the causative agent that causese the otitis. Middle ear infections are the most prevalent childhood ailment. The age group of 6 months to 2 years old is the most common for ear infections in children. Because there eustachian tubes aren't working as well as fluid is more likely to build up behind the eardrum. Their immune system, which are also developing and Otitis media comes in various forms, such as the following:
Medial otitis acute: This middle ear infection comes on suddenly, resulting in redness and edema. The youngster has a fever and ear ache when fluid and mucus get stuck within the ear.
Effusion-associated otitis media: The accumulation of mucus and fluid (effusion) in the middle ear persists even after the underlying infection is resolved.This could have an impact on their hearing.
Effusion in chronic otitis media: There is no infection, yet fluid stays in the middle ear for a long time or keeps coming back. may make it harder for the youngster to fight off future infections and could have an impact on their hearing.
Symptoms
- Ear pain
- Tugging or pulling at an ear
- Trouble sleeping
- Crying more than usual
- Fussiness
- Trouble hearing or responding to sounds
- Loss of balance
- Drainage of fluid from the ear
- Headache
Causes/Risk factors
- Age
- Family history
- Colds
- Chronic illness
- Poor air quality
- Smoky environment
Diagnosis
Cytology department
Cytological examination is performed along with the microscope. The specimen is obtained from the patient. With the help of a cotton swab, the pus sample is removed from the ear. Then colonies grow on the culture plate. After the colonies grow on the culture plate, then prepare the glass slide of the culture and also use the staining technique. Gram staining plays a vital role in revealing the morphology of the bacteria.
Streptococcus pneumoniae in Gram Staining
Microbiology department
The pus sample is removed from the ear. Make it dilution and grow on culture plate. After the incubation period, the colonies grow on the the media plate. Take a small colony of the bacteria, spread on the glass slide and stain it. After the staining process is completed, then observed under the microscope.
Microbiology examination of Streptococcus pneumoniae
Reference:-
1.https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8613-ear-infection-otitis-media
2.https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=otitis-media-middle-ear-infection-90-P02057
0 comments