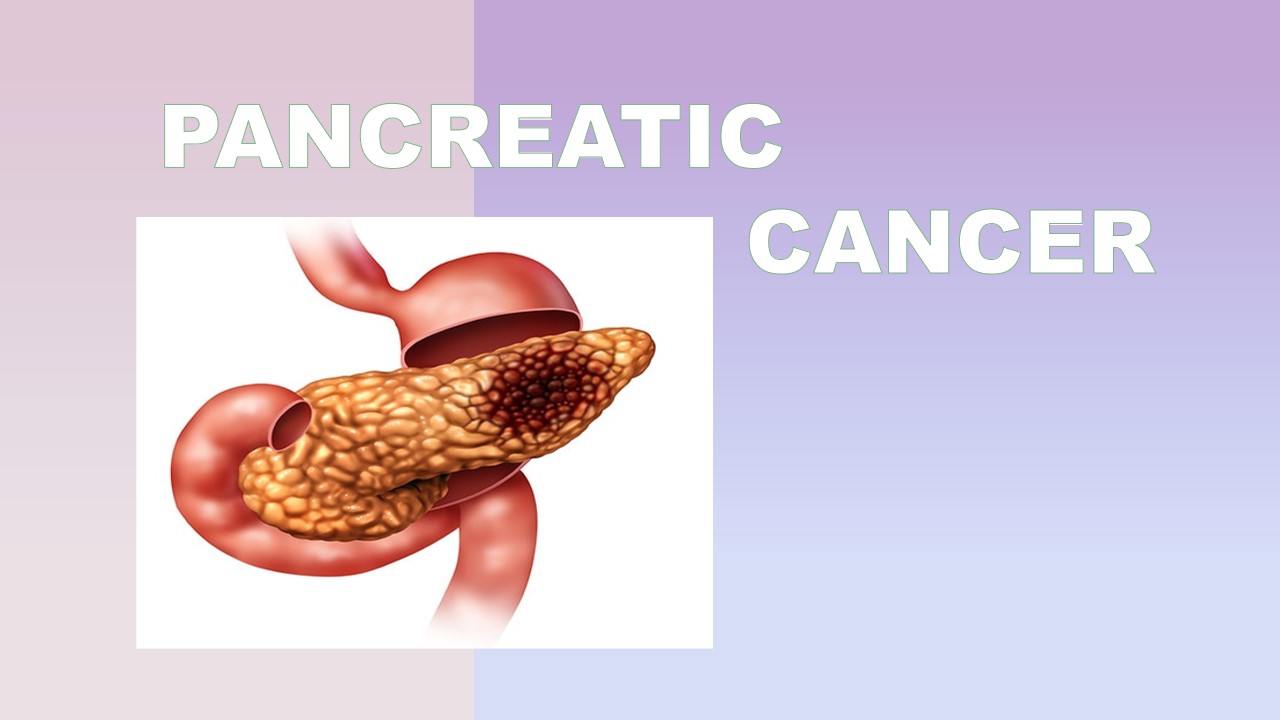
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer is a cancer of the pancreas. The same abbreviation of pancreatic cancer is pancreatic adenocarcinoma. The pancreas is an important organ of the body. The pancreas is an elongated, tapped organ located on the back of the belly, behind the stomach. The pancreas is made up of two types of glands such as exocrine and endocrine gland. The exocrine gland produces digestive enzyme, which helps to breakdown the carbohydrates, proteins, fats and acid in the duodenum. The endocrine gland produces hormones into the bloodstream. The main hormones insulin and glucagon are secreted by the pancreas,which regulates the blood glucose level.
Pancreatic cancer is uncontrolled growth of the cells in the pancreas. Two broad categories can be used to categorize the many forms of pancreatic cancer. Approximately 95% of instances are located in the exocrine component of the pancreas, which is responsible for producing digestive enzymes. There are numerous exocrine pancreatic cancer sub-types identified, yet there are many similarities in their diagnosis and course of treatment.Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors are the rare type of cancer that develop in the hormone-producing (endocrine) tissue of the pancreas; they differ in their clinical features.
Symptoms
- Belly pain
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- jaundice
- Light-colored or floating stools
- Dark-colored urine
- Itching
- New diagnosis of diabetes or diabetes that's getting harder to control
- Pain and swelling in an arm or leg
- Tiredness or weakness
Causes/Risk factors
- von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
- Lynch syndrome
- cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver
- infection of the stomach
- diabetes
- obesity
- chronic pancreatitis, or inflammation of the pancreas
- smoking
Diagnosis
Cytology department
A catheter is inserted into the bile duct and brushing and washing is performed to collect the fluid and cells for microscopy examination. Then the specimen was smeared on a slide, fixed it and hematoxylin and eosin stains apply on the smeared slide, observed under the microscope.
Cytology of bile duct Brushings
Histology department
Histopathology examination is essential for accurate diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. In which tissue biopsy as a specimen is used for diagnosis. The pathologist examines the specimen's external features, noting the size, location, and any abnormalities. The tissue is processed, embedded in paraffin, and sliced into thin sections for microscopic evaluation.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with H and E stain
Reference:
1. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15806-pancreatic-cancer
2. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pancreatic-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20355421
0 comments